Lattice vibration
LATTICE VIBRATION:-
Every atom has a tendency to vibrate about their mean position at temperature above zero Kelvin. The mean position is referred as the Bravais lattice site . These vibrations occur due to interatomic interactions. As the atoms in the solids are present at lattice sites , so these vibrations are called lattice vibrations.
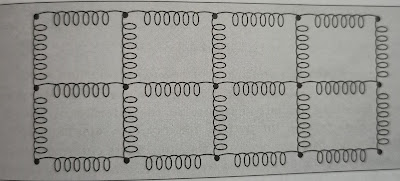 |
| Fig.1 |
Lattice vibration are the results of absorption of heat energy. A lattice is an array of atoms connected with each other by elastic springs or strings .
Here all the atoms present at lattice sites are coupled and the motion of one single atom is shared by the neighbouring atoms. Thus the crystal vibrates on a whole . The dynamic external forces which are responsible for the vibrations obey Hooke's law. It is assumed that the amplitude of the vibrations are small as compared to the interatomic spacing. Harmonic approximation is valid for lattice vibrations. Thus every atom present at lattice sites is considered to be as harmonic oscillator.
According to quantum theory , the energy E of an elastic mode of vibration of angular frequency when the mode is excited to a quantum number n is given as
 To understand the lattice vibration, let us revise interatomic forces near the neighbourhood of equilibrium separation about which the atoms vibrate. The interatomic forces may be attractive or repulsive depending upon the separation between the two atoms.
To understand the lattice vibration, let us revise interatomic forces near the neighbourhood of equilibrium separation about which the atoms vibrate. The interatomic forces may be attractive or repulsive depending upon the separation between the two atoms.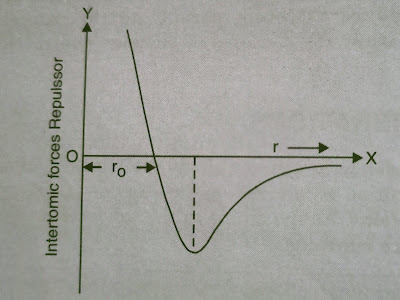 |
| Fig.2 |
At normal distance r, the two atoms are placed at equilibrium space . Any increase or decrease in their separation, need some energy. An increase in the interatomic separation r1 leads to attractive force and similarly decrease in the interatomic separation r1 leads to repulsive force . For NaCl crystal, the normal distance r is approximately 1 which is of same order as the distance from the centre of the atom to its outermost electrons. As the Na and Cl atoms exists in a regular array, when we try to deform the solid by external force , the strong interatomic forces between the atoms resist compression or extension.
A regular lattice with harmonic forces between atoms and normal modes of vibration are called lattice waves. Lattice waves have frequency from low value to high values of the order 10Hz . The wavelength corresponding to high frequency are comparable to the interatomic spacing. Due to short wavelength the motion of the neighbouring atoms is uncorrelated, with each atom vibrating about mean position in three dimensions with average vibrations energy. The electrical resistance in the conducting solids arise due to the interaction of lattice vibration with free electrons.
The theories of lattice vibration are associated with the specific heat of solids . These vibrations influence several physical properties of solids as follows:
 |

Comments
Post a Comment